Business Permits and Licences
Starting a business in Kenya requires obtaining various permits and licenses to ensure compliance with the legal and regulatory framework. These permits and licenses are essential for operating legally and smoothly in the country. Understanding the different types of permits and licenses required is crucial for aspiring entrepreneurs and foreign investors to navigate the process effectively.
1. Business Registration: Registering your Business with the Registrar of Companies.
The Registrar of Companies in Kenya oversees the registration of businesses. This office issues various certificates:
- Certificates of compliance for foreign companies.
- Certificates of incorporation for local companies and partnerships.
- Certificates of registration for sole proprietorships .
To streamline the process, the Business Registration Services (BRS) has integrated name reservation and company registration into a single procedure.
It's important to note that all company and business registrations are conducted through the official government eCitizen portal. This online platform provides a centralized and accessible method for business registration in Kenya.
READ MORE : Types of Business Entities in Kenya
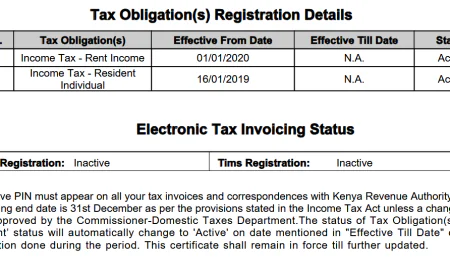
2. Tax Compliance Certificate: Ensuring Compliance with Tax Regulations.
Upon business or company registration, obtain a Tax Personal Identification Number (PIN) and taxpayer certificate for the company and directors from the Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA).
Register with the KRA to pay taxes such as Corporate Income, Value Added Tax (VAT), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), and any other required obligations based on the company's services.
Tax obligations for Kenyan businesses may include ;
- Corporate Income Tax,
- Value Added Tax (V.A.T)
- Pay As You Earn (PAYE)
- Rent Income
- Withholding Tax
- Excise Duty
- Customs Tax
- Digital Service Tax
- Capital Gains Tax, and
- Turnover Tax.
Kenya Investment Authority facilitates investors to get a KRA PIN without having a foreign national registration certificate (alien card) by giving them an endorsement letter that they should present to KRA to obtain both Individual and company PINs.
3. Social Security and Employees Deductions NSSF, NHIF,NITA and Affordable Housing Remittance Deductions.
Social security and employee deductions are integral components of the employment system in numerous countries, including Kenya. In the Kenyan context, these deductions encompass several key elements:
- National Health Insurance Fund (NHIF): Employers must provide healthcare coverage, including mandatory NHIF membership. Employers deduct contributions from employee salaries. Employers may offer private medical insurance to employees in addition to the public NHIF remittance.
- National Social Security Fund (NSSF) : Both employers and employees must contribute equally to this pension and social security fund.
- National Industrial Training Authority (NITA) Levy: Companies must pay KSh. 50 per employee per month to the National Industrial Training Authority.
- Affordable Housing Levy: Employers must deduct a portion of employee salaries and remit it to the housing fund.
4. County Business Permits : Obtaining the Necessary Approval for Business Establishment.
Kenyan counties have implemented a streamlined approach to business licensing through the issuance of single business trade licenses or unified permits.
The specific permit type is determined by various factors, including the business's location, number of employees, nature of operations, and activities.
The unified permit system is designed to simplify the licensing process by consolidating multiple permits into one comprehensive document. For instance, in Nairobi County, a unified business permit may encompass several certifications, such as:
- Fire clearance certificate
- Advertising signage approval
- Health certificate
- Food hygiene certification
- Pest control verification
The application process offers flexibility to businesses. Applicants have the option to submit their applications and make payments online. However, it's important to note that the fee assessment is conducted in person. Alternatively, applicants can choose to submit their applications in person to obtain the unified permit.
Once an application is submitted, county officials undertake a thorough review process. This evaluation may involve several steps, including:
- Site inspections
- Verification of provided information
- Compliance assessments
This comprehensive review ensures that businesses meet all necessary regulatory requirements before the unified permit is issued.
5. Trade Licences: Ensuring Compliance with Sector-Specific Regulations that apply to your business.
Trade licenses in Kenya ensure compliance with sector-specific regulations that govern various business activities and regulated industry sectors.
The process of acquiring a trade license in Kenya involves identifying the specific sector or industry in which the business operates and then applying for the corresponding license.
This can range from different regulated industry sectors such as:
- Manufacturing sector
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT
- Energy sector - Petroleum licences
- Agricultural sector
- Tourism sector
- Mining sector
- Financial Services
- Import Export
- Construction
6. Intellectual Property and Copyright : Protecting your intellectual property, trademarks, copyright and Patents.
The registration of a business name with the Companies Registry in Kenya does not automatically provide trademark protection, even if the business name and trade name are identical.
It is essential to conduct a thorough search for similar existing trade names and trademarks at the Kenya Industrial Property Institute (KIPI) before proceeding with registration.
Intellectual property protection is fundamental for safeguarding your brand, innovation, or creation. This can be achieved by searching for or applying to register exclusive rights for an invention, product, or process.
In Kenya, the Kenya Copyright Board (KECOBO) is responsible for administering and enforcing copyright and related rights. KECOBO offers several services to businesses seeking copyright registration, including:
- Copyright registration
- Copyright enforcement
- Copyright legal advice
- Maintenance of a comprehensive databank containing information on authors and their works.
These services are designed to help businesses protect their intellectual property and ensure compliance with copyright laws in Kenya.
7. Hiring and Managing Employees : Register the workplace with the Directorate of Occupational Safety and Health Services
Before any person or business occupies or uses any premises as a workplace, they must apply for registration by sending an assessment application to the Director of Occupational Safety and Health Services.
It is an offense for anyone to occupy or use any premises as a workplace without first obtaining a certificate of registration.
A business can register to obtain a certificate for:
- Workplaces e.g., offices, public buildings, farms, stores
- Plants e.g., factories and industries.
These registration licenses are issued to ensure that every workplace is free of hazards and complies with established standards to ensure employee safety.
8. Export Processing Zones : Investment opportunity for export-oriented business ventures
Kenya's Export Processing Zones (EPZs) provide significant investment opportunities for businesses focused on exports.
These zones offer a flexible ownaership structure, allowing for 100% foreign ownership, 100% Kenyan ownership, or a combination of both. Additionally, companies are permitted to bring in foreign workers for training, technical, and managerial positions.
Several key licenses are available for businesses operating within EPZs:
- EPZ Manufacturing Enterprise License: This annual renewable license is for companies engaged in manufacturing or processing activities for export.
- EPZ Commercial Enterprise License: Issued annually to companies involved in commercial activities such as bulk breaking, repackaging, re-labeling, and trading for export purposes.
- Developer Operator License: This license is granted to entities developing infrastructure and buildings for new zones intended for EPZ enterprises.
- EPZ Service Enterprise License: Issued to companies providing export-oriented services, including brokerage, information, consultancy, and repair services.
- EPZ Business Service Permit: This non-transferable, one-year permit is for service activities within an EPZ by firms that do not require or qualify for an EPZ enterprise license.
Eligible activities for EPZ business service permit include:
- Commercial banking
- Clearing and forwarding
- Catering and restaurant services
- Recruitment and payroll services
- Postal and telecommunication services
- Office services
- Transportation services
- Installation, repair, and maintenance
- Fitness, sports, and gymnasium facilities
- Medical and related services
- Laboratory, testing, and quality certification
- Security services
- Business consultancy (e.g., marketing, training, legal)
- Insurance services
- Foreign trade missions
- International disaster relief agencies and NGOs
These licenses and permits facilitate a wide range of business activities within Kenya's EPZs, creating a conducive environment for export-oriented enterprises.
9. Work Permits and Passes: For foreign nationals looking to work or do business in Kenya
Kenya has established specific regulations for the employment of foreign nationals within its borders. These regulations encompass several key elements:
- Valid Visas: Foreign workers must possess appropriate visas or travel authorization.
- Foreign National Registration: Expatriates are required to obtain Foreigner Certificate (Alien Card) .
- Permits: Specific permits are necessary for foreign nationals to work legally in Kenya.
- Passes: Certain passes may be required depending on the nature of work and stay.
For companies intending to hire foreigners in Kenya:
- It is mandatory to secure proper work permit approvals.
- This typically involves obtaining a work permit from the Immigration Department prior to the employee's arrival in the country.
For expatriates planning to live and work in Kenya:
- Appropriate work permits and passes must be obtained before entering the country.
- The application process varies based on the nature and duration of the planned stay.
These regulations are designed to ensure legal compliance and proper documentation for foreign workers in Kenya.
10. Health and Environmental Permits: Obtaining permits related to health or environmental concerns.
In Kenya, health and environmental permits play an important role in safeguarding public health and protecting the environment. These permits are mandatory for businesses and a person whose activities may impact these areas.
1. Health Permits
- Food service establishments require specific health permits.
- Business premises must undergo inspection to ensure they are fit for purpose and have adequate hygiene facilities.
- Workers in the food service industry must obtain health clearance certificates.
2. Environmental Licenses and Permits
The National Environmental Management Authority (NEMA) issues various permits and licenses, including:
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) License: Required for activities that may affect the environment, such as construction, waste management, and use of hazardous materials.
- Noise permits for events
- Waste management licenses for garbage collectors
- Effluent discharge permits
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) is a key requirement for activities that could potentially impact the environment.
Some activities may require additional permits beyond the standard environmental permit. For instance, mining operations need a license from the Ministry of Petroleum and Mining to operate.
11. Professional Licences: Meeting the Requirements for Practicing Professions.
Foreign nationals seeking to provide professional services in Kenya must familiarize themselves with the relevant legal statutes governing their profession.
Obtaining the appropriate license is important, as it verifies that a person has fulfilled the required education and training standards to offer services in their respective fields.
Various professional bodies oversee different sectors in Kenya. For instance:
- Engineering firms must register with the Engineers Board of Kenya (EBK).
- Accounting firms are required to register with the Institute of Certified Public Accountants of Kenya (ICPAK).
- Professionals in Architecture and Quantity Surveying must register with the Board of Registration of Architects and Quantity Surveyors (BORAQS).
- Legal service providers need to be registered with the Law Society of Kenya.
These professional memberships serve two primary purposes.
- They ensure that practitioners adhere to industry standards.
- They provide a level of credibility for clients seeking professional services.
By complying with these regulations, foreign professionals can establish their legitimacy in the Kenyan market and operate within the legal framework of their chosen field.
12. Useful Links
Was this information helpful ?
 Like
3
Like
3
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
3
Love
3
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
1
Sad
1
 Wow
2
Wow
2