Resident Income Tax
An overview of income tax in Kenya for resident individuals. The essential information you need to know about income tax according to the Kenyan law.
1. Understanding the Basics of Resident Income Tax in Kenya
Resident income tax is a type of income tax imposed upon a resident person or a person having a permanent establishment in Kenya with an income from sources accrued in or derived from Kenya.
2. Who is Considered a Resident for Income Tax Purposes in Kenya?
In Kenya, an individual is considered a resident for tax purposes if they have a permanent home in the country or spend at least 183 days in any given year within its borders.
Also an individual must have been present in the country for more than 122 days in that year of income, as well as in each of the two preceding years of income, with the periods averaging more than 122 days in each year of income.
3. Types of Income Subject to Resident Income Tax in Kenya
The most common types of taxable income sources in Kenya is derived from:
- Business income.
- Employment income.
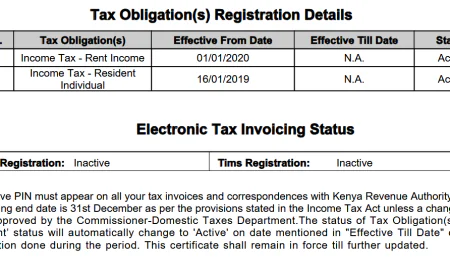
- Rent Income.
- Investment income such as dividends and interests.
- Digital marketplace income.
- Management and professional fees.
4. The Kenyan Resident Income Tax Rates and Brackets
In Kenya, resident individuals are subject to a progressive income tax system, which means that higher income earners are taxed at a higher rate compared to those with lower incomes. The income tax rates range from 10% to 35%, depending on the individual's annual earnings.
|
Monthly Taxable Pay (Ksh) |
Annual Taxable Pay (Ksh) |
Tax Rate % |
|
Up to 24,000 |
288,000 |
10% |
|
8,333 |
100,000 |
25% |
|
467,667 |
5,612,000 |
30% |
|
300,000 |
3,600,000 |
32.5% |
|
32,333 |
9,600,000 |
35% |
5. Deductions and Allowances for Residents under the Kenyan Income Tax System
The Kenyan income tax system provides various deductions and allowances for residents to reduce their taxable income. These deductions and allowances are designed to incentivize certain activities, promote investments, and provide relief to taxpayers and minimize their tax liability.
One of the key deductions available to residents is the
- Personal Relief : This allowance is a fixed amount that can be deducted from an individual's taxable income before calculating the final tax liability. The personal relief allowance aims to provide a basic level of exemption for individuals, taking into account their personal circumstances such as age, marital status, and disability.
- Insurance Relief : Another tax relief for personal income is the Insurance relief which is based on premiums paid for education policies, health policies or life insurance for resident individuals respectively.
- Affordable Housing Relief : Affordable housing relief is eligible to a resident individual who is under a government affordable housing scheme.
In addition to the personal relief, insurance and affordable housing allowance, residents can also benefit from specific deductions such as:-
- Deductions related to expenses incurred in earning income : For example, individuals who contribute towards a registered pension scheme or retirement annuity fund can claim a deduction for these contributions. This encourages individuals to save for their retirement while reducing their taxable income.Residents may also be eligible for deductions related to mortgage interest payments on owner-occupied homes or investment properties. These deductions aim to promote homeownership and encourage investment in real estate.
- Investment-related allowances : Residents who invest in certain sectors or engage in specific activities may be eligible for investment allowances that allow them to deduct a portion of their investment costs from their taxable income. These investment-related allowances aim to stimulate economic growth by incentivizing investments in priority sectors identified by the government.
It is worth noting that while these deductions and allowances can significantly reduce an individual's tax liability, they are subject to certain conditions and limitations imposed by the Government and Kenyan Revenue Authority (KRA).
It is essential for residents seeking these benefits to fully understand the eligibility criteria, documentation requirements, and any restrictions associated with each deduction or allowance.
6. Filing Requirements and Deadlines for Residents' Income Tax Returns
Residents, defined as individuals who have been physically present in Kenya for at least 183 days in a tax year or are considered to have a permanent home in the country, are required to file their income tax returns annually. This includes individuals who earn income from employment, business, rental properties, or any other sources.
The deadline for filing income tax returns for residents in Kenya is typically on or before 30th June of the following year. For example, if you earned income during the 2021 calendar year, you would need to file your tax return by 30th June 2022. It's important to note that failure to meet this deadline may result in penalties and interest charges imposed by the Kenya Revenue Authority (KRA).
To file your income tax return as a resident in Kenya, you will need various supporting documents such as your KRA PIN (Personal Identification Number), copies of your monthly payslips or salary statements if employed, bank statements if self-employed or running a business, rental agreements if earning rental income, and any other relevant financial records.
Filing of income tax return is done on an online platform called iTax which allows residents to conveniently file their income tax returns electronically. This platform provides step-by-step guidance and simplifies the process of submitting accurate information.
It's worth noting that certain exemptions and reliefs may apply depending on individual circumstances such as disability status, or specific industries. Therefore, it is advisable to consult with a qualified tax professional or refer to official guidelines provided by the KRA for detailed information on eligibility criteria and available deductions.
Late filling penalties is charged at a rate of 5% of the tax due or Kshs. 2,000 and interest rate of 1% per month on the unpaid tax.
7. In Conclusion
By understanding the filing requirements and deadlines for residents' income tax returns in Kenya, individuals can ensure compliance with tax laws and avoid unnecessary penalties. It is always recommended to stay updated with any changes or updates from the KRA to fulfill your tax obligations effectively.
Was this information helpful ?
 Like
0
Like
0
 Dislike
0
Dislike
0
 Love
0
Love
0
 Funny
0
Funny
0
 Angry
0
Angry
0
 Sad
0
Sad
0
 Wow
0
Wow
0